
Visualizing How Military Blasts Impact Unborn Babies
Pictured: Assistant Professor Milan Toma
A recent study by College of Osteopathic Medicine (NYITCOM) faculty and alumni provides new insight into how military blasts can injure unborn babies (fetuses) and how the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus may provide protection. The findings, which were published in the journal Injury, could help doctors better assess fetal injuries and inform the development of future safety devices.
Pregnancy-related trauma is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in pregnant women and their unborn babies. Recently, military conflicts in Eastern Europe and the Middle East, where there have been documented cases of airstrikes targeting maternity hospitals, have led scientists and medical professionals to consider how the forces of a military blast could impact unborn children.
Now, researchers, led by biomedical engineer and NYITCOM Assistant Professor Milan Toma, Ph.D., have used elaborate 3-D models to simulate the impact of an explosion beneath a motor vehicle. The models accounted for real patient-specific geometries and fluid-structure interaction in spaces between the inner lining of the uterus and fetus, placenta, and umbilical cord.
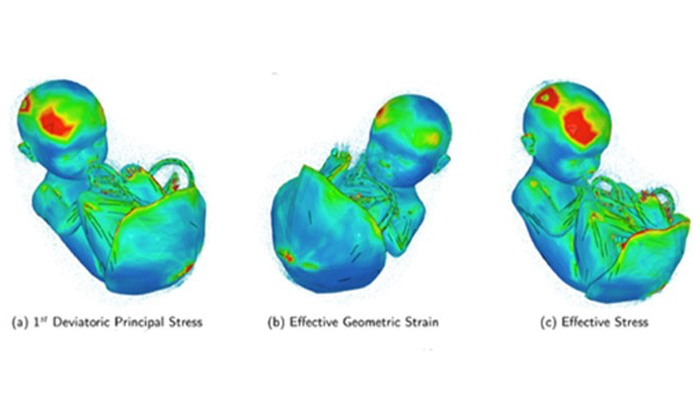
Their findings showed that amniotic fluid is crucial in protecting the fetus from trauma. While the simulated explosion subjected the outside of the uterus to multiple acceleration changes, the fetus (inside the uterus) experienced lesser acceleration changes. The models also showed that because the fetus was positioned with its head facing down and exposed to an explosion underneath the mother’s womb, the area around the skull sustained more stress.
The study was conducted in collaboration with Jonathan Arias (D.O. ’23) and Gregory Kurgansky (D.O. ’23), former NYITCOM students who have since completed their studies and advanced to residency programs. Other collaborators included Ong Chi Wei, Ph.D., from Singapore’s Institute of High Performance Computing, and Rosalyn Chan-Akeley, M.D., an OB-GYN affiliated with Lang Research Center at New York-Presbyterian Hospital Queens.
More Features

Building Bridges
New York Tech students earned first place at the 2026 KEEN Bridge Design Competition for their outstanding bridge design and structural efficiency.

NOMA Competition: Reimagining Kansas City
Twelve architecture students competed in the 2025 Barbara G. Laurie Student Design Competition sponsored by the National Organization of Minority Architects (NOMA) to propose a model for housing that prioritizes those vulnerable to racialized disinvestment.

Making an Impact
As an ETIC engineer, computer science student Angelina Do is working on a project in partnership with a former NBA star aimed to help children who stutter.

Realistic 3-D Colon Model Shifts Paradigm for Drug Development
Assistant Professor Steven Zanganeh, Ph.D., is striving to further improve the model he developed to open the door to drug development for cancer and other conditions.

Additional Alumni Named to Board of Trustees
Two New York Institute of Technology alumni have been named to the Board of Trustees, the most recent alumni to join the university’s governing board.

Celebrate Black History Month 2026
New York Tech celebrates Black History Month with a series of events.